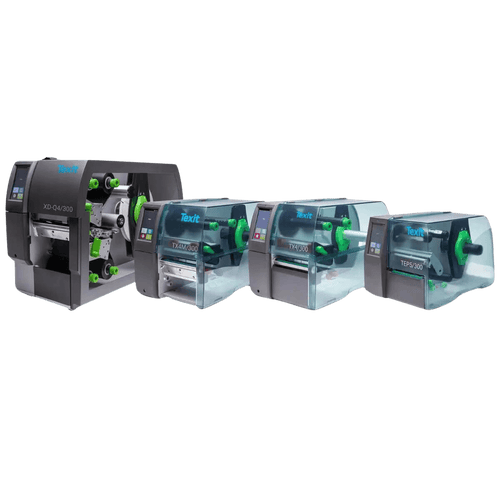
Our 4 Texit printers in comparison
How does a thermal transfer printer work?
With a thermal transfer label printer, the heat melts the ink from the thermal transfer foil, also known as ribbon, onto the material to be printed. The high temperature causes the ink particles to bond firmly with the label/marker. This is where the name thermal transfer printing comes from - a print created by heat transfer. This transfer takes place inside the printer, more precisely at the print head. A large number of small, computer-controlled heating elements are located there, which enable precise, high-quality printing on paper and plastic. A sensor in the printer detects the position of the material to be printed and can precisely control the heating elements based on the specified print layout.
Thermal transfer printer label preparation
In thermal transfer printing, it is important that both the printer and the ribbon are precisely matched to the material to be printed. This is the only way to achieve high-quality printing results. At the beginning of the printing process, the material to be printed must first be placed on the holder and inserted into the material guide. Then the ribbon must also be placed on the holder provided. From there, about 30 cm of ribbon is unwound and attached to the roll core with an adhesive strip. This way, the used ribbon is directly rewound during the printing process. The ribbon must be firmly tensioned on both the unwinder and the rewinder
.
The winding of the printing material and the ink ribbon is particularly important. There are internally and externally wound material and ribbon. Both variants can be used with all Texit thermal transfer printers without any problems, however, when loading the material / ribbon, attention must be paid to the guide. In general, the material guide on the print head must always be aligned upwards, while the ink-carrying layer on the ribbon must be aligned downwards. A corresponding exploded view with a detailed illustration of the guide is included with every Texit printer. Another important point is the sensor positioning. If the material to be printed does not pass through the light barrier without interference, it will be detected incorrectly or not at all by the printer.
After the material and the ribbon have been placed correctly in the printer, the print head can now be closed. Finally, by pressing the "FEED" button on the printer, the material to be printed is calibrated and the zero point is thus automatically adjusted. If no error messages are shown in the display, printing can be started.
Texit thermal transfer printer functions
Texit thermal transfer printer models
As we at Texit specialize in industrial marking using thermal transfer printers, we have various printer devices in our range. All products have a print resolution of 300 dpi, are suitable for higher print volumes and are easy to change ribbons. Our small printer is also suitable as a desktop printer due to its light weight and compact size. All printers are compatible with the new Texit Designer 11 software(label printer with software).
Thermal transfer label printer
With the Texit thermal transfer printer labels, both thermal transfer labels and cable markers can be printed permanently and flexibly. This printer model impresses with its low price and versatility: It can also be used to print labels in continuous format. We recommend this printer primarily for occasional use. It is also suitable as a desktop printer as it is compact and lightweight. It can therefore be easily taken to the construction site during transportation.
Cable labeling printer
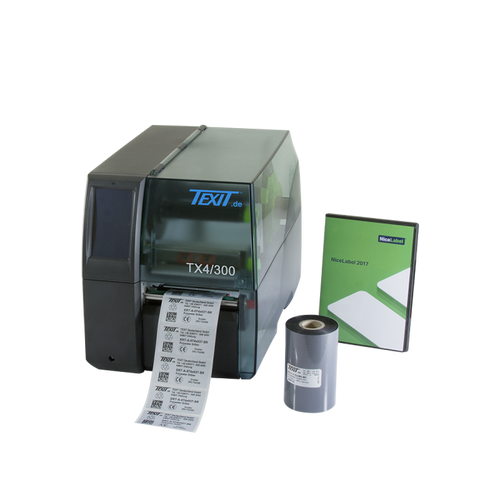
With the TX4 cable marking printer, you can not only print cable markings, but also thermal transfer labels. This thermal transfer printer is ideal for long-term use in industry as it is very flexible. With a print speed of up to 300 mm/s, it quickly delivers high-quality and permanently legible marking for cables, wires, lines, machines and systems as well as labels for machine marking and equipment identification.
Thermal transfer printer heat shrink tubing
The TX4M shrink tubing printer is ideally suited for professional printing of all types of shrink tubing in industry. Just like the cable label printer, the Texit TX4M has a robust metal housing and scores particularly well on the subject of flexibility (labels and cable markers can also be easily printed permanently with this printer). As a shrink sleeve printer, the TX4M can also print continuous material without any problems.
Direct thermal printing vs. thermal transfer printing
Both direct thermal and thermal transfer printing are processes in the thermal printing category. In both processes, printing is done with the help of selective heat. The difference between the two types of printing is that no ink is used in the direct thermal process.
Only specially treated material can be printed using this process. The heat triggers a chemical reaction in the material, which then changes color. The print results come exclusively from this chemical reaction. This is why it is not possible to choose from different colors with the direct thermal process. In addition, the print is not very durable and therefore less suitable for permanent marking. However, it is more cost-effective than thermal transfer printing.
Thermal transfer printers use special ribbons made of wax, resin or a mixture of both materials. The color is melted / transferred from the ribbon to the label / cable marker to be printed by the selective application of heat. This produces very durable and robust printing results.
Advantages of the thermal transfer process
The thermal transfer process has many advantages for permanent marking. As the effect of heat melts the ink from the thermal transfer ribbon onto the material, a new robust layer is created on the material. The printing results are extremely durable (if the ribbon and the material to be printed are well matched) and are still easily legible even under heavy loads.
The print remains scratch and smudge-proof even when it comes into contact with oils, petrol or alcohol. In addition, the ribbon can be used in the desired color, meaning that colored prints are also possible. Many different materials can be printed on with the thermal transfer printer without having to be specially treated beforehand. The printing process can therefore be used very flexibly in various sectors of industry.
Which materials can be printed with the thermal transfer printer?
A major advantage of thermal transfer printers is that a wide variety of materials can usually be printed on with one printer. In general, paper, textile fabric and plastic are equally suitable for thermal transfer printing. However, as paper labels are not suitable for permanent marking, we will take a closer look at the various plastics and textile fabrics here.
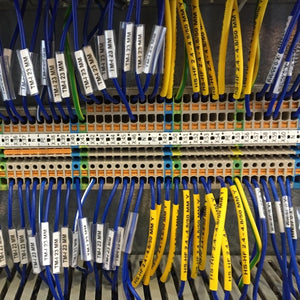
Labels and cable markers made of plastic are particularly suitable for the permanent marking of machines, systems and cables. They are robust, durable and high-quality print results can be achieved using the thermal transfer process. Each of the plastic types listed below can be labeled very well with a thermal transfer printer. The choice of suitable thermal transfer ribbon depends on the type of plastic. For permanent marking, it is important that the type of plastic matches your requirements and that the thermal transfer printing system is optimized for the material to be printed on.
Thermal Transfer Printer Applications & Use
Thanks to their versatility, thermal transfer printers are used in many technical areas. Due to the high print quality and consistency of the print results, they are very well suited for industrial use. A thermal transfer printer can be used to print on paper and textile fabrics as well as various types of plastic.
The most common areas of application for thermal transfer printers are:
- Durable Cable labelling
- Printing of machine signs
- Printing of industrial labelsespecially barcode labels for product labeling
- Printing of warning signs and (tamper-proof) test badges
Get in touch with us quickly and easily
Still have questions about thermal transfer printers?
Our labeling experts will be happy to advise you personally and 100% without obligation
Thermal Transfer Printer FAQ
How does a thermal transfer printer work?
How does a thermal transfer printer work?
A thermal transfer printer works by selectively heating a ribbon to transfer dyes to a print medium such as labels. The printer has a ribbon that is coated with dye (wax/resin coating). This ribbon is located between the print head and the print medium. The print head consists of many small heating elements that are selectively heated. The ink layer of the ribbon melts in the heated areas and adheres to the print medium, while the ink remains on the ribbon in the unheated areas. The ribbon and the print medium continue to move synchronously, which means that the printing process is continuous.
How long does thermal transfer printing last?
How long does thermal transfer printing last?
Under optimum conditions, thermal transfer printing provides a print image that is legible for more than 10 years! To produce such a print image, it is important that the ribbon matches the material to be printed and that the temperature setting on the printer is correct. The service life of the printed image also depends on the print medium used. With a thermal transfer label printer with a resolution of at least 300 dpi and the correct matching of ribbon and material, you can achieve such a print quality without any problems.
What is the difference between thermal transfer and direct thermal?
What is the difference between thermal transfer and direct thermal?
The difference between the thermal transfer and direct thermal processes is that thermal labels are made from a heat-sensitive material and are printed directly by applying heat. In thermal transfer printing, on the other hand, the ink is transferred from a ribbon to the material to be printed on by heating. The melted ink layer bonds permanently with the carrier material of the marking.
As a result, you are more limited in your choice of materials for direct thermal printing. In return, however, you also need a ribbon (on rolls) for printing with the thermal transfer printer.
Where are thermal printers still used today?
Where are thermal printers still used today?
Thermal printers are characterized by their simple design and are inexpensive to purchase. They do not require a ribbon, but do need special, usually expensive thermal paper, which yellows over time. This can cause prints to fade or become difficult to read after around six months. While thermal printers were previously often used in fax machines, today they are mainly used in cash register systems, ticket machines and shipping labels. These are the typical papers that can be found faded somewhere in the house after months.
Today, thermal printers are only used to a very limited extent in industry.