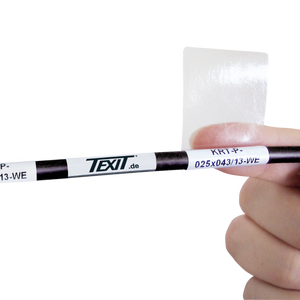
Labeling for machines made easy: With just one printing system, you can take complete labeling into your own hands
The marking of machinery is a key aspect of industrial and manufacturing environments, with multiple implications for safety, efficiency and compliance. It not only serves to identify machines and their components, but also plays a crucial role in communicating safety information and complying with legal regulations.
Structured machine marking helps to ensure that maintenance, repair and servicing work can be carried out efficiently. The relevant machinery directives (e.g. Eg directives such as the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC ) must be complied with so that you, as a manufacturer in the machinery and plant engineering sector, can bring safe products onto the market or, as an operator, ensure that your employees can handle the machinery safely. Structured marking therefore involves much more than just the CE mark or CE marking.
On this page, we have created an overview of all the key points of machine marking with a Texit printing system. We are also happy to offer you support in selecting the right marking. In a personal meeting with our marking experts, we will clarify your requirements and start planning together. This keeps the effort for your company very low and at the same time ensures that your marking complies with the standards and obligations of the industry.
✔️ CE marking & safety marking compliant with Machinery Directive 2006 42 EC
✔️ Flexible labeling of different machine components with just one printing system
✔️ Nameplates, cable labeling & safety signs
✔️ Efficient troubleshooting through easy identification of individual components & parts
✔️ Time & cost savings for subsequent maintenance / repair & replacement work.
✔️ Easy assembly during installation
✔️ Wide range of extremely robust products with long service life
✔️ Benefit in the long term from our Texit service & our many years of expertise in the field of machine labeling
CE marking Machines Nameplates
Type plates are important components of the machine marking and contain specific information about the machine itself as well as information on conformity with the applicable regulations. The CE mark itself is a mandatory part of the marking and must be affixed to the machine to indicate that it complies with the applicable EU directives.
At Texit you have the opportunity to purchase inexpensive and at the same time extremely robust nameplate labels. Not only do you benefit from the lower price compared to conventionally engraved aluminum nameplates, but you can also print your own nameplates in the future.
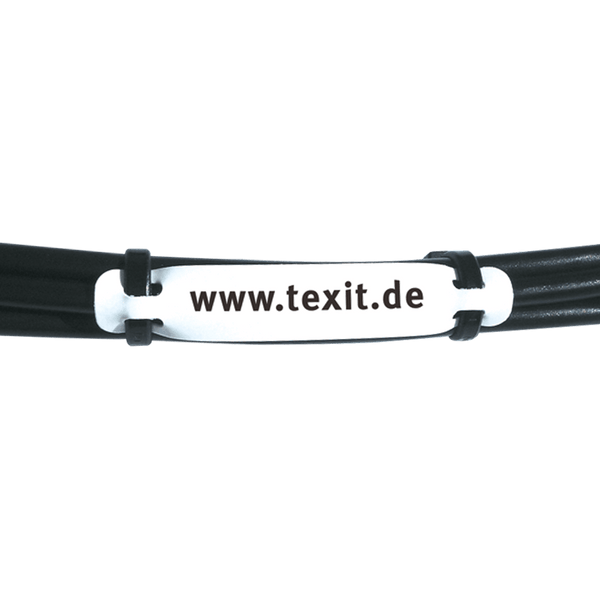
Labeling machines Cable labeling
Clear and unambiguous cable labeling helps to identify various electrical connections and components in a machine. This makes troubleshooting and maintenance easier, as maintenance personnel can quickly locate the correct cables and connections. Clear cable labeling reduces the risk of mix-ups or incorrect connections that could lead to malfunctions or damage to the machine. This contributes to the reliability and operational safety of the machine.
With cable labeling from Texit, you are on the safe side: whether shrink sleeves, cable markers, cable labels or cable clips. Our labeling experts will advise you in detail on your requirements and the applicable standards and specifications.
Safety labeling for machinery and plant engineering
The marking of machines makes a significant contribution to safety in the workplace by warning employees of potential hazards and providing clear instructions for safe operation. Legally required inspection stickers are also used in the field of safety marking. At Texit, we are happy to help you with a free, personal consultation on optimal safety marking.
Looking for more machine marking products?
Discover our entire range of labeling for machines.
We make labeling for machines easy
Marking machines can be quick, easy and uncomplicated. At Texit, we guarantee our customers a special service in addition to excellent product quality. You will be assigned a trained expert as a permanent contact person who will advise you on the right products and will also look after you afterwards, solving problems and optimizing the use of our products on site at your premises.
As an ISO-certified company, you can rely on our 20 years of experience in the field of industrial labelling.
Labeling for machines FAQ
Which machines need a CE marking?
Which machines need a CE marking?
The CE marking is an important feature for a large number of machines and devices that are sold or used within the European Economic Area (EEA) (i.e. also for operators or the importer). In general, all machines and devices that fall under the EU Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) require a CE marking in accordance with the EC Machinery Directive before they can be placed on the market. This applies to a wide range of machines and devices, including
- Industrial machines: Machines used in factories and production facilities, such as production lines, processing machines, presses, robots, etc.
- Construction and construction site machinery: machinery used for construction and construction site activities, such as excavators, cranes, concrete mixers, road construction machinery, etc.
- Agricultural machinery: machinery used in agriculture, such as tractors, combine harvesters, sprayers, harvesters, etc.
- Electrical and electronic devices: Electrical and electronic machines and devices that must meet certain safety standards, such as household appliances, machine tools, medical devices, etc.
- Vehicles: Certain types of vehicles and their components that are not covered by specific vehicle directives, such as agricultural vehicles, forklift trucks, mobile machinery, etc.
It is important to note that not all machines and appliances require a CE mark. Some specialized machines or those intended for private use (operation for personal use only) may be exempt from the CE marking requirement. However, if in doubt, it is advisable to refer to the relevant regulations and directives or consult a technical expert. This is because the Machinery Directive also differs depending on the machines and systems and different requirements must be met by companies depending on the Machinery Directive.
When is CE marking mandatory?
When is CE marking mandatory?
CE marking is mandatory in the European Union (EU) for a large number of products and machines when they are placed on the market or used (i.e. also for operators). In general, CE marking is mandatory if a product falls under one or more EU directives that require CE marking. We have listed the most important factors that determine when CE marking is required:
- Scope of application of the EU directives: The CE marking obligation arises from various EU directives, such as the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), the EMC Directive (2014/30/EU) and others. A product must meet the requirements of one or more of these directives in order to bear the CE marking.
- Product category: CE marking is required for a wide range of products and machinery, including industrial machinery, construction and site machinery, electrical and electronic equipment, toys, medical devices, personal protective equipment, elevators, pressure equipment and more.
- Compliance with safety standards: Products must meet certain health and safety requirements set out in the relevant EU directives. This includes aspects such as electrical safety, mechanical safety, health protection, environmental protection and more.
- Placing on the market or use within the European Economic Area (EEA): The CE marking is required for products that are placed on the market or used in the European Economic Area (EU member states as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway).
- Manufacturer's responsibility: It is the manufacturer's responsibility to ensure that their product complies with the applicable EU directives and that the CE marking is affixed correctly. This includes carrying out a risk assessment, drawing up a declaration of conformity and complying with the relevant technical requirements.
Overall, CE marking is an important requirement for products sold or used in the EU and serves to ensure the safety of consumers and workers and to facilitate the free movement of goods in the European Single Market. If you have any questions about CE marking, you should always consult an expert!
When does a machine lose its CE marking?
When does a machine lose its CE marking?
A machine loses the CE marking if it no longer complies with the applicable EU directives and regulations or if changes are made to the machine that affect its conformity with these directives. This point is therefore also important for machine operators and not just for machine manufacturers. We have listed the most common situations that can lead to a machine losing its CE marking:
- No longer compliant with the directives: If the machine or its components change in such a way that they no longer meet the requirements of the applicable EU directives, the CE marking may lose its validity. This may be the case, for example, if the machine no longer complies with the health and safety requirements of the directives due to modifications or deterioration.
- Missing or expired conformity assessment: The CE marking requires a conformity assessment to prove that the machine complies with the applicable EU directives. If the conformity assessment is missing or has expired and has not been renewed, this may result in the loss of the CE marking.
- Missing or insufficient documentation: Adequate documentation is an important part of the CE marking. If the required documents, such as the technical documentation, declaration of conformity or EC declaration of conformity, are missing or incomplete, this may result in the CE marking losing its validity.
- Non-compliance of the manufacturer: The manufacturer is responsible for compliance with the applicable EU directives and the correct affixing of the CE marking. If the manufacturer does not fulfill his obligations or provides false information, this may result in the CE marking being withdrawn.
- Incorrect use of the CE marking: The CE marking must not be used in a misleading or incorrect manner. Falsely affixing the CE marking to a machine when it does not comply with the applicable EU directives can have legal consequences and invalidate the CE marking.
Overall, it is important that manufacturers ensure that their machines continuously comply with the applicable EU directives and that the CE marking is and remains properly affixed to ensure the safety of consumers and workers and to meet legal requirements. In particular, the requirements for CE certification must be met.
Which devices need a CE mark?
Which devices need a CE mark?
A large number of products and devices (not only machines or in mechanical engineering) require the CE mark before they can be sold or used in the European Economic Area (EEA). We have listed some examples of devices and products that may require CE marking:
- Electrical and electronic equipment: This includes a wide range of products such as household appliances (e.g. washing machines, refrigerators), consumer electronics (e.g. televisions, radios), computers and peripherals, power tools, toys with electrical components and more.
- Machines and industrial equipment: Industrial machines, machine tools, machining centers, presses, hoists, conveyors, welding equipment, packaging machines, robotic systems and other machines used in industrial processes.
- Medical devices: Diagnostic devices, medical imaging systems, ventilators, medical laboratory equipment, surgical instruments, implants and other medical devices intended for use in medical facilities.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Safety equipment such as helmets, safety goggles, hearing protection, respirators, protective gloves, safety shoes and other products designed to protect the user from injury or health hazards.
- Toys: Toys for children of all ages, including toys with electronic or mechanical components, soft toys, dolls, toy vehicles, building blocks and more.
- Construction products: Construction products such as windows, doors, bricks, insulation materials, paints, ladders and other building materials that must comply with the requirements of the Construction Products Regulation (EU) 305/2011.
- Pressure equipment: Pressure vessels, compressed air tanks, steam boilers and other pressure equipment that must meet certain safety requirements.
This list is not exhaustive as there are many other product categories that may also require CE marking. In general, all products that fall under the applicable EU directives and are marketed or used in the EEA must meet the relevant requirements and bear the CE mark. The exact requirements depend on the EC directives or machines and systems, and apply to both manufacturers and operators in plant construction.